Resource
Supporting Communication for Learners who are Deaf-Blind and/or have Multiple Disabilities
This document was created to help teams to think about how best to support communication for learners who are deafblind or who have multiple disabilities.
This document was created by the New York Deaf-Blind Collaborative to help teams to think about how best to support communication for learners who are deafblind or who have multiple disabilities. There is a space for student notes at the end of each section.
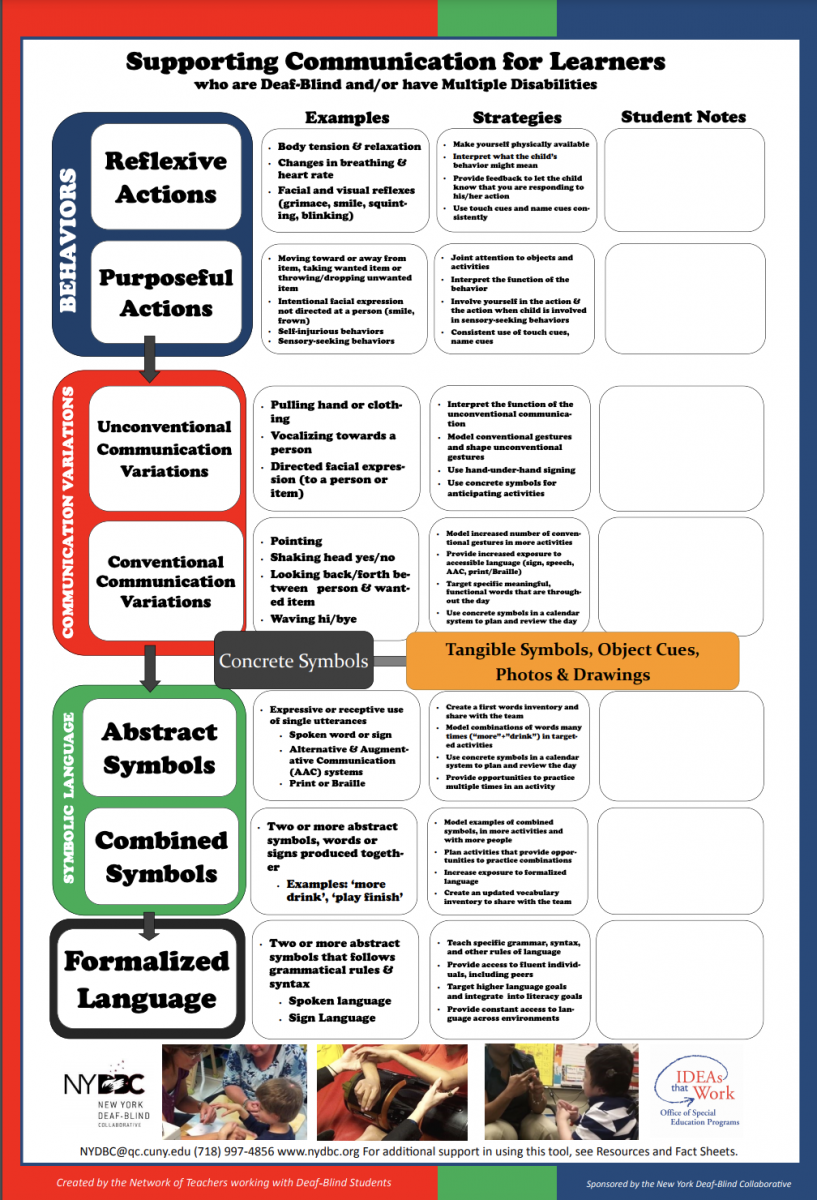
Behaviors
- Reflexive Actions
- Examples:
- Body tension & relaxation
- Changes in breathing & heart rate
- Facial and visual reflexes (grimace, smile, squinting, blinking)
- Strategies
- Make yourself physically available
- Interpret what the child’s behavior might mean
- Provide feedback to let the child know that you are responding to his/her action
- Use touch cues and name cues consistently
- Purposeful Actions
- Examples:
- Moving toward or away from item, taking wanted item or throwing/dropping unwanted item
- Intentional facial expression not directed at a person (smile, frown)
- Self-injurious behaviors
- Sensory-seeking behaviors
- Strategies:
-
Joint attention to objects and activities
-
Interpret the function of the behavior
-
Involve yourself in the action & the action when child is involved in sensory-seeking behaviors
-
Consistent use of touch cues, name cue
-
Communication Variations
- Unconventional Communication Variations
- Examples:
-
Pulling hand or clothing
-
Vocalizing towards a person
- Directed facial expression (to a person or item)
-
- Strategies:
- Interpret the function of the unconventional communication
- Model conventional gestures and shape unconventional gestures
- Use hand-under-hand signing
- Use concrete symbols for anticipating activities
-
- Conventional Communication Variations
- Examples:
- Pointing
- Shaking head yes/no
- Looking back/forth between person & wanted item
-
Waving hi/bye
-
- Strategies
-
Model increased number of conventional gestures in more activities
-
Provide increased exposure to accessible language (sign, speech, AAC, print/Braille)
- Target specific meaningful, functional words that are throughout the day
- Use concrete symbols in a calendar system to plan and review the day
-
Concrete Symbols: Tangible Symbols, Object Cues, Photos & Drawings
Symbolic Language
- Abstract Symbols
- Examples
- Expressive or receptive use of single utterances
- Spoken word or sign
- Alternative & Augmentative Communication (AAC) systems
- Print or Braille
- Strategies
- Create a first words inventory and share with the team
- Model combinations of words many times (“more”+”drink”) in targeted activities
- Use concrete symbols in a calendar system to plan and review the day
- Provide opportunities to practice multiple times in an activity
- Examples
- Combined Symbols
- Examples
- Two or more abstract symbols, words or signs produced together; Examples: ‘more drink’, ‘play finish’
- Strategies
- Model examples of combined symbols, in more activities and with more people
- Plan activities that provide opportunities to practice combinations
- Increase exposure to formalized language
- Create an updated vocabulary inventory to share with the team
- Examples
Formalized Language
- Examples:
- Teach specific grammar, syntax, and other rules of language
- Provide access to fluent individuals, including peers
- Target higher language goals and integrate into literacy goals
- Provide constant access to language across environments
- Strategies
- Teach specific grammar, syntax, and other rules of language
- Provide access to fluent individuals, including peers
- Target higher language goals and integrate into literacy goals
- Provide constant access to language across environments